Basic Business Needs:
- Use a single installation of any Oracle Applications product to support any number of organizations, even if those organizations use different sets of books.
- Define different organization models.
- Support any number of legal entities within a single installation of Oracle Applications.
- Secure access to data so that users can access only the information that is relevant to them.
- Sell products from a legal entity that uses one set of books and ship them from another legal entity using a different set of books, and automatically record the appropriate intercompany sales by posting intercompany accounts payable and accounts receivable invoices.
- Purchase products through one legal entity and receive them in another legal entity.
Basically the different entities in multi-org are:
- Business Group (BG)
- Sets of Books (SOB)
- Legal entities (LE)
- Operating units (OU)
- Inventory organizations (IO)
Organization Structure Example:
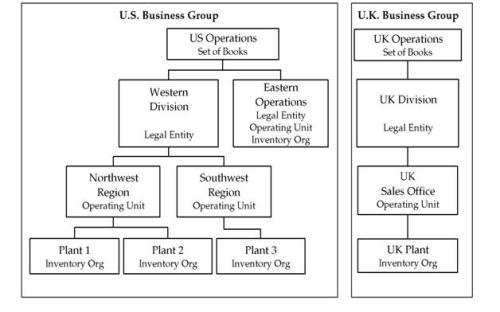
Business Group (BG):
The business group represents the highest level in the organization structure, such as the consolidated enterprise, a major division, or an Operation Company. A BG is used to secure human resources information like generation of employee numbers, generation of applicants, position flex fields, Job flexfields, Grade Flex field, Fiscal year, etc.
Set of Books (SOB):
A SOB is a collection of Currency, Calendar and Chart of Accounts (COA). Oracle General Ledger is used to secure Journal transactions (such as journal entries and balances) of a company by set of books. For each organization of the Business Group we need to define a set of Book. A company which operates in separate cities or separate line of businesses may separate their accounting transactions across units through separate Set of Books. A Business Group can have one or more set of Books.
Legal entities (LE):
A legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. You assign tax identifiers and other legal entity information to these types of organizations. Separate Legal Entities may share same set of Books.
Operation Unit (OU):
An operating unit is a division or a Business unit of the legal entity. At this level we are going to maintain the information of sub‐ledgers. We are going to maintain the ledgers at Legal Entity level. Receivable, Payables, Assets, etc. are comes under Operation Unit level. Each user sees information only for their operating unit. Responsibilities are linked to a specific operating unit by the MO: Operating Unit profile option.
Inventory organizations (IO):
An inventory organization represents an organization for which you track inventory transactions and balances, and manufactures or distributes products. Examples include manufacturing plants, warehouses, distribution centers, and sales offices. The following products and functions secure information by inventory organization: Inventory, Bills of Material, Engineering, Work in Process, Master Scheduling/MRP, Capacity, and purchasing receiving functions. To run any of these products or functions, you must choose an organization that is classified as an inventory organization.

Recent Comments